
Goods and Services
American.gov | 2013-01-24 12:55
(The following article is taken from the U.S. Department of State publication, USA Economy in Brief.)
A national economy comprises a country's production of goods and services. Real gross domestic product (GDP) measures such output produced by labor and property in the United States.
Workers use capital and natural resources to produce goods and services. Natural resources are those supplied by planet Earth: air, water, trees, coal, soil.
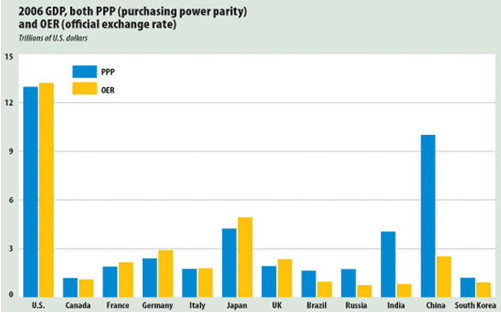
By various measures, the United States accounts for 20 to 30 percent of world Gross Domestic Product.
Americans produce what the world needs and wants
Capital includes physical capital: tools, machines, technology (high and low). It includes intellectual property: copyrights, patents, trademarks. It includes human capital: training, skills, experience.
Capital includes physical capital: tools, machines, technology (high and low). It includes intellectual property: copyrights, patents, trademarks. It includes human capital: training, skills, experience.
Most natural resources in the United States come from land privately owned by individuals or corporations or leased from governments at the national and state levels. Governments set rules for using natural resources, such as controlling pollution.
The United States is rich in mineral resources, although it has already passed the point of peak production for some, including oil. It has much fertile farm soil and a moderate climate. It has extensive coastlines on the Atlantic and Pacific oceans and the Gulf of Mexico. Rivers flow from far within the continent and the five Great Lakes on the border with Canada provide additional shipping access. Extensive waterways, railroads, highways, and air transportation shape the 50 individual states into a single economic unit.
Individuals or corporations own most U.S. technology and other physical capital. The U.S. economy is especially rich in information technology, accounting for major gains in productivity over the past decade. Governments set rules for buying, selling, and using capital.
Individuals, corporations, universities, and other research institutions own intellectual property. Worldwide theft of U.S. copyrighted films, music CDs, and software, as well as patented designs, is estimated at billions of dollars a year.
Since the United States abolished slavery during the Civil War in 1863, all U.S. workers own their own labor and are free to sell it to employers for wages or work for themselves – self-employment. Governments set rules for hiring and employing workers.
To produce goods and services, business managers organize and direct labor, capital, and natural resources in response to market signals. In a traditional business structure, management works through a top-down chain of command. In a typical factory, for example, authority flows from the chief executive, who aims to run the entire business efficiently, through lower levels of management down to the foremen on the shop floor.
Some businesses use a more flexible organization, especially in high-technology industries where skilled workers develop, modify, and customize products rapidly. These companies have "flattened" their organizations, reducing the number of managers and delegating more authority to interdisciplinary teams of workers. Often teams form to carry out a project and then disband when the project is completed, with team members moving to new challenges with other groups.
So what does the U.S. economy actually produce?
Share this page



















