Educational stages in the U.S.
WIKIPEDIA | 2014-05-22 15:18
Formal education in the U.S. is divided into a number of distinct educational stages. Most children enter the public education system around ages five or six. They may begin in preschool, kindergarten or first grade. They normally attend 12 grades of study over 12 calendar years of primary/elementary and secondary education before graduating, earning a diploma that makes them eligible for admission to higher education. Education is only mandatory until age 16, however. There are generally five years of primary (elementary) school, during which students customarily advance together from one grade to the next as a single cohort or "class", three years of middle school, which may have cohorts, and four years of high school. There is some variability in the arrangement of grades.
In the U.S., ordinal numbers (e.g., first grade) are used for identifying grades. Typical ages and grade groupings in contemporary, public and private schools may be found through the U.S. Department of Education. Generally there are elementary school (K-5th grade), middle school (6th-8th grades) and high school (9th-12th grades). Many different variations exist across the country.
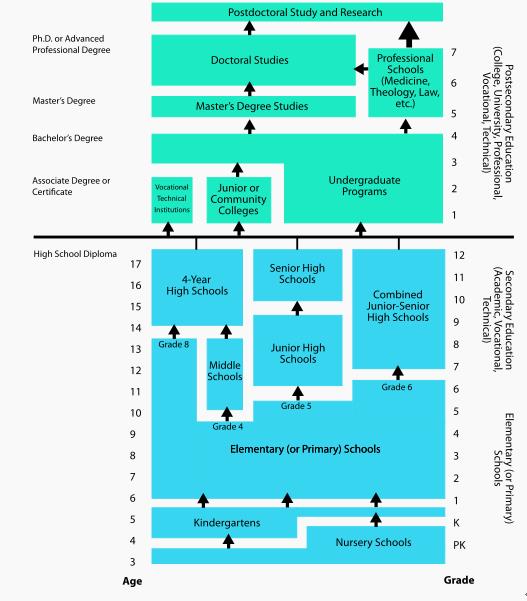
Students completing high school may choose to attend a college or university, which offer undergraduate degrees such as Associate's degrees or Bachelor's degrees (baccalaureate).
Community college or junior college typically offer two-year associate's degrees, although some community colleges offer a limited number of bachelor's degrees. Some community college students choose to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a Bachelor's degree. Community colleges are generally publicly funded (usually by local cities or counties)and offer career certifications and part-time programs.
Four-year institutions may be public or private colleges or universities.
Some counties and cities have established and fund four-year institutions; examples include the City University of New York, City Colleges of Chicago, and San Francisco City College.
Private institutions are privately funded and there is a wide variety in size, focus, and operation. Some private institutions are large research universities, while others are small liberal arts colleges that concentrate on undergraduate education. Some private universities are nonsectarian and secular, while others are religiously-affiliated. While most private institutions are non-profit, a growing number in the past decade have been established For-profit education.
Curriculum varies widely depending on the institution. Typically, an undergraduate student will be able to select an academic "major" or concentration, which comprises the main or special subjects, and students may change their major one or more times.
Some students, typically those with a bachelor's degree, may choose to continue on to graduate or professional school. Graduate degrees may be either master's degrees (e.g., M.A., M.S., M.B.A.,M.S.W.) or a doctorates (e.g., Ph.D., J.D., ("Doctor of Law"), M.D., D.O.). Academia-focused graduate school typically includes some combination of coursework and research (often requiring a thesis or dissertation to be written), while professional graduate-level schools (e.g., medical, law, business) grants a first professional degree and aims to prepare students to enter a learned profession of a medical doctor, attorney at law (lawyer), advanced Business/Economics. Other graduate-level schools attached to many Universities train for a Pharmacist, dentist, veterinarian, or minister/priest. Normally it's 4 years college/university. Community and special colleges may offer 2 year degrees so that would be any range from age 18 to 20(normally).
In the U.S., ordinal numbers (e.g., first grade) are used for identifying grades. Typical ages and grade groupings in contemporary, public and private schools may be found through the U.S. Department of Education. Generally there are elementary school (K-5th grade), middle school (6th-8th grades) and high school (9th-12th grades). Many different variations exist across the country.

| General level (or category) | Level | Student age range | |||||||
| Preschool | Pre-kindergarten | 2–4 | |||||||
| Compulsory education | |||||||||
|
Elementary school |
Kindergarten | 5–6 | |||||||
| First grade | 6–7 | ||||||||
| Second grade | 7–8 | ||||||||
| Third grade | 8–9 | ||||||||
| Fourth grade | 9–10 | ||||||||
| Fifth grade | 10–11 | ||||||||
|
Middle school |
Sixth grade | 11–12 | |||||||
|
Junior high school |
Seventh grade | 12–13 | |||||||
| Eighth grade | 13–14 | ||||||||
|
High school |
Freshman/9th Grade | 14–15 | |||||||
|
Senior high school |
Sophomore/10th Grade | 15–16 | |||||||
| Junior/11th Grade | 16–17 | ||||||||
| Senior/12th Grade | 17–18 | ||||||||
| Higher education | |||||||||
|
College (University) |
Undergraduate school |
Freshman year |
Ages vary, but often 18–22 for a consecutive bachelor's degree (usually within a solitary concentration) |
||||||
| Sophomore year | |||||||||
| Junior year | |||||||||
| Senior year | |||||||||
|
Graduate school (with various degrees and curricular partitions thereof) |
Ages vary | ||||||||
| Continuing education | |||||||||
| Vocational school | Ages vary | ||||||||
| Adult education | |||||||||
Students completing high school may choose to attend a college or university, which offer undergraduate degrees such as Associate's degrees or Bachelor's degrees (baccalaureate).
Community college or junior college typically offer two-year associate's degrees, although some community colleges offer a limited number of bachelor's degrees. Some community college students choose to transfer to a four-year institution to pursue a Bachelor's degree. Community colleges are generally publicly funded (usually by local cities or counties)and offer career certifications and part-time programs.
Four-year institutions may be public or private colleges or universities.
Some counties and cities have established and fund four-year institutions; examples include the City University of New York, City Colleges of Chicago, and San Francisco City College.
Private institutions are privately funded and there is a wide variety in size, focus, and operation. Some private institutions are large research universities, while others are small liberal arts colleges that concentrate on undergraduate education. Some private universities are nonsectarian and secular, while others are religiously-affiliated. While most private institutions are non-profit, a growing number in the past decade have been established For-profit education.
Curriculum varies widely depending on the institution. Typically, an undergraduate student will be able to select an academic "major" or concentration, which comprises the main or special subjects, and students may change their major one or more times.
Some students, typically those with a bachelor's degree, may choose to continue on to graduate or professional school. Graduate degrees may be either master's degrees (e.g., M.A., M.S., M.B.A.,M.S.W.) or a doctorates (e.g., Ph.D., J.D., ("Doctor of Law"), M.D., D.O.). Academia-focused graduate school typically includes some combination of coursework and research (often requiring a thesis or dissertation to be written), while professional graduate-level schools (e.g., medical, law, business) grants a first professional degree and aims to prepare students to enter a learned profession of a medical doctor, attorney at law (lawyer), advanced Business/Economics. Other graduate-level schools attached to many Universities train for a Pharmacist, dentist, veterinarian, or minister/priest. Normally it's 4 years college/university. Community and special colleges may offer 2 year degrees so that would be any range from age 18 to 20(normally).
Share this page