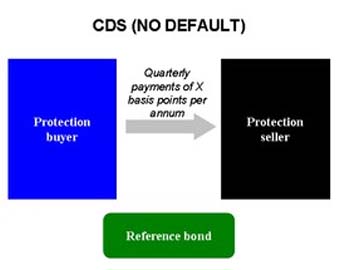
If the reference bond performs without default, the protection buyer pays quarterly payments to the seller until maturity If the reference bond defaults, the protection seller pays par value of the bond to the buyer, and the buyer transfers ownership of t
full story >>Quantitative easing (QE) is an unconventional monetary policy used by central banks to stimulate the economy when standard monetary policy has become ineffective.[1][2][3] A central bank implements quantitative easing by buying specified amounts of long t
Continue reading >>Probability of default (PD) is a financial term describing the likelihood of a default over a particular time horizon. It provides an estimate of the likelihood that a client of a financial institution will be unable to meet its debt obligations.[1][2] PD
Continue reading >>Robert Shiller's plot of the S&P composite real price–earnings ratio and interest rates (1871–2012), from Irrational Exuberance, 2d ed.[1] In the preface to this edition, Shiller warns that "the stock market has not come down to historical levels
Continue reading >>The price-to-book ratio, or P/B ratio, is a financial ratio used to compare a company's current market price to its book value. It is also sometimes known as a Book-To-Market ratio.
Continue reading >>An open market operation (also known as OMO) is an activity by a central bank to buy or sell government bonds on the open market. A central bank uses them as the primary means of implementing monetary policy.
Continue reading >>